Course Description
This course covers key competencies in the different facets of managing a project, including managing team and client interactions. Students will learn essential skills from the ability to provide structure at the foundling stages of the project, to estimating and projecting budgets, as well as developing and managing a project timeline for ensured project success.
Prerequisites
Recommended Textbook(s)
- Goto, Kelly and Emily Cotler. Web ReDesign 2.0 | Workflow that Works. Grand Rapids: New Riders, 2004.
- Friedlein, Ashley. Web Project Management: Delivering Successful Commercial Web Sites. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 2000.
- Berkun, Scott. Making Things Happen. Sebastopol: O'Reilly Media, Inc., 2009.
- Cohn, Mike. Agile Estimating and Planning. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2005.
- Wiefling, Kimberly. Scrappy Project Management: The 12 Predictable and Avoidable Pitfalls Every Project Faces. Cupertino: Happy About, 2007.
- Garton, Colleen, and Erika McCulloch. Fundamentals of Technology Project Management. New York: Mc Press, 2005.
Recommended Reading
Please see the Assignments for the corresponding recommended readings.Technologies Required
Software or hardware requirements:
- text editor
- project management tool (online)
- time-tracking and invoicing tool (online)
- timeline/gantt chart tool (open source)
Competencies
| Project phase | Topic¹ | Competency | Evaluation (assignments) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ¹pm=Project Management, cm=Client Management, tm=Team Management | |||
| 0-pm foundations | all |
|
All assignments |
| 1-initiation | pm |
|
Project Brief |
| 1-initiation | pm |
|
Risk Planning Workshop |
| 1-initiation | pm |
|
Project Timeline |
| 1-initiation | pm |
|
Project Timeline |
| 1-initiation | pm |
|
Chinese Whispers |
| 2-kick-off | cm |
|
Project Kickoff |
| 2-kick-off | cm |
|
Communication Quadrant |
| 2-kick-off | cm |
|
Project Kickoff |
| 2-kick-off | tm |
|
Internal project kick-off meeting |
| 2-kick-off | tm |
|
Continual project assessment |
| 3-implementation | cm |
|
Using communications |
| 3-implementation | tm |
|
Skills evaluation |
| 3-implementation | cm | Create a project hand-off document | Hand-off document |
| 3-implementation | pm |
|
Continual project assessment |
| 4-completion | pm |
|
Hand-off document, weekly status reports |
| 4-completion | tm |
|
Post-mortem |
| 5-all | cm, pm, tm |
|
Weekly status reports |
Assignments
Project Brief
Assignment: Project plan & brief
Section: Team management
Phase: Kickoff
Type: Project support documentation
Goals
Students learn how to create a real-world deliverable: a project brief that facilitates clarifying the project definition for both the client and the internal team. Students begin to conceptualize the project and what is involved early in the process. Students learn to create a document that serves as an accountability tool for the team, the project manager and the client.
Readings
- Sample RFP
- Communication brief worksheet
- Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow That Works, Chapters 2, 3, 10
- Web Project Management, Chapter 4
- Scrappy Project Management, Chapter 5
- Making Things Happen, Chapters 7, 15
Assignment
1. Write a description of the project (approximately 600 words). Include:
- Project purpose: who is the client? what is the purpose of the project? what are its business goals?
- Project scope: what are we producing?
- Project sponsors & stakeholders: who are the major decision-makers who have sign-off capacity? What is their contact information?
- Success criteria & quality definition: are these your criteria of success or the client’s criteria?
- Project constraints, assumptions and dependencies.
- Resources: what human resources, technologies, applications and tools do we have?
- Project budget
- Milestones
- project time/cost estimation: what is the proposed estimated project length? How many hours will it take to complete the project within budget in the given amount of time? What is the preliminary estimated timeline for the project?
2. Describe the process you will use to address this project and what are the key reasons for doing so. You can choose to describe either waterfall, modified waterfall or an agile process.
- what are the phases of the project?
- what can the client expect from the project team during each phase?
- what are the expectations and responsibilities of the client during each phase?
- what will be the project deliverables?
3. Describe what solution you will implement in order to fulfill the project goals (approximately 500 words).
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project purpose and scope | The project purpose is well defined: the client is described well, the scope of the project and the project goals are clear and understandable. | The project purpose is mostly defined: the client is described moderately, the scope of the project and the project goals are mostly clear and understandable. | Some of the project purpose is defined: the client is described only partially, the scope of the project and the project goals are partially clear and understandable. | Little if any of the project purpose is defined: the client description is inaccurate, the scope of the project and the project goals are unclear and difficult to understand. |
| Stakeholders / sponsors | All of the stakeholders/sponsors have accurate and complete contact information. | The stakeholders/sponsors have accurate and mostly complete contact information. | Some stakeholders/sponsors have accurate and mostly complete contact information. | Few if any of the stakeholders/sponsors have accurate and complete contact information. |
| Success criteria and quality definition | The success criteria is itemized, accurate and complete. | The success criteria is itemized, mostly accurate and mostly complete. | The success criteria is itemized, partially accurate and somewhat complete. | The success criteria is poorly itemized, potentially inaccurate and incomplete. |
| Project constraints, assumptions and dependencies | Project constraints are clearly and comprehensively outlined, complete with assumptions and dependencies. | Project constraints are clearly outlined, complete with assumptions and dependencies. | Project constraints are partially outlined, with some assumptions and dependencies. | Project constraints not poorly outlined, with some assumptions and dependencies. |
| Resources | Resources are comprehensively listed. | Resources are mostly listed. | Resources are partially listed. | Resources are incomplete. |
| Budget | The project budget is itemized, accurate and complete. | The project budget is itemized, mostly accurate and mostly complete. | The project budget is itemized, partially accurate and somewhat complete. | The project budget is poorly itemized, potentially inaccurate and incomplete. |
| Milestones | Milestones are comprehensively indicated. | Most milestones are indicated. | Milestones are partially indicated. | Some or few milestones are indicated. |
| Time/cost estimation | The time/cost estimations are clear and accurate. | The time/cost estimations are mostly clear and accurate. | The time/cost estimations are only partially clear and accurate. | The time/cost estimations are only unclear and of questionable accuracy. |
| Process | The explanation of the project process is clear, easy to understand, and follows a natural progression. Roles and participation of parties involved is clearly explained. | The explanation of the project process is fairly clear, moderately understandable, and mostly follows a natural progression. Roles and participation of parties involved is moderately explained. | The explanation of the project process is only partially clear and understandable, and only slightly follows a natural progression. Roles and participation of parties involved are not fully explained. | The explanation of the project process is unclear and not understandable, and only does not follow a natural progression. Roles and participation of parties involved are unclear or not explained. |
| Project solution proposal | Description is clear, concise and states what activities that will be undertaken, as well as an appropriate technological solution. | Description is clear, concise, mentioning most activities that will be undertaken, as well as an appropriate technological solution. | Description is vague, too long (or too short) mentioning some activities that will be undertaken and a fairly appropriate technological solution. | Description is vague, too long (or too short) mentioning some activities that will be undertaken and an inappropriate technological solution. |
| Presentation | The scope document is well-organized, consistently formatted, and has a very professional presentation/look and feel. | The scope document is mostly organized and consistently formatted, and has a moderately professional presentation/look and feel. | The scope document is only somewhat organized and consistently formatted, and has a slight professional presentation/look and feel. | The scope document is poorly organized and inconsistently formatted, and completely lacks a professional presentation/look and feel. |
Risk Planning Workshop
Assignment: Risk planning workshop
Section: Team management
Phase: Kickoff
Type: project support documentation
Goals
Students learn to anticipate, prioritise and plan for risks.
Readings
Assignment
- Brainstorm sources of Risk to the project - anything that might negatively impact the project constraints. Choose two approaches from: documentation reviews, assumptions analysis, checklists, SWOT analysis, stakeholder interviews.
- Assess each Risk as High/Medium/Low on dimensions of Probability and Impact. Rank the list of risks.
- For the top 5 Risks, define:
- the trigger (how you will know the Risk is becoming a reality)
- a response for coping with the Risk and description for how it will help
- an owner for monitoring the trigger & implementing the Response
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Identification | Risk sources are comprehensively covered, including external dependencies and assumptions. Risk descriptions are clear, concise, states their causes and impacts in a way that can be easily quantified/ranked. | Risk sources include external dependencies and assumptions. Risk descriptions are concise, cause and impacts are clear, but not easily quantified/ranked. | Risk sources miss either external dependencies or assumptions. Risk descriptions identify either cause or impact reasonably clear but are not easily quantified/ranked. | Risk sources miss both external dependencies and assumptions. Risk descriptions of cause and impact are vague, too long (or too short) and not quantified/ranked. |
| Risk Analysis | Ranking is complete. It clearly and correctly differentiates the most significant Risks. | Ranking is complete. Risks are significantly mis-ranked (either too high or too low). | Ranking is complete. Risks poorly differentiated, or most are at a similar level (either high or low). | Ranking is incomplete; many Risks un-evaluated. |
| Risk Response Planning | Each priority risk’s trigger & response is clear, concise, falls appropriately into one of the strategy categories and adequately plans the activities to be undertaken and by whom | Each priority risk’s trigger & response is clear, falls appropriately into one of the strategy categories and partially plans the activities to be undertaken and by whom. | Priority risks’ trigger is clear, but response is vague, while falling into one of the categories (even if not appropriate). Response activities are partial, but do have owners. | Priority risks’ trigger is vague, response is vague and does not clearly fall into a strategy category. Response Activities do not have owners. |
Project Timeline
Assignment: Project Timeline
Section: Project management
Phase: Initiation
Type: Group brainstorm & project support documentation
Class organisation suggestion
The teacher assigns rotating roles of class members to create teams that include at least:
- one project manager
- one graphics designer
- one user experience designer
- one front-end engineer
- one back-end developer
Readings
- Sample RFP
- Web ReDesign 2.0: Workflow that Works, Chapter 2 & 3
- http://www.agile-software-development.com/2008/01/example-of-user-story.html
- Agile Estimating and Planning, Parts II, III and IV or User stories applied: Chapters 8–11
- Critical Path Drill (Headfirst Labs)
Planning Activities flow
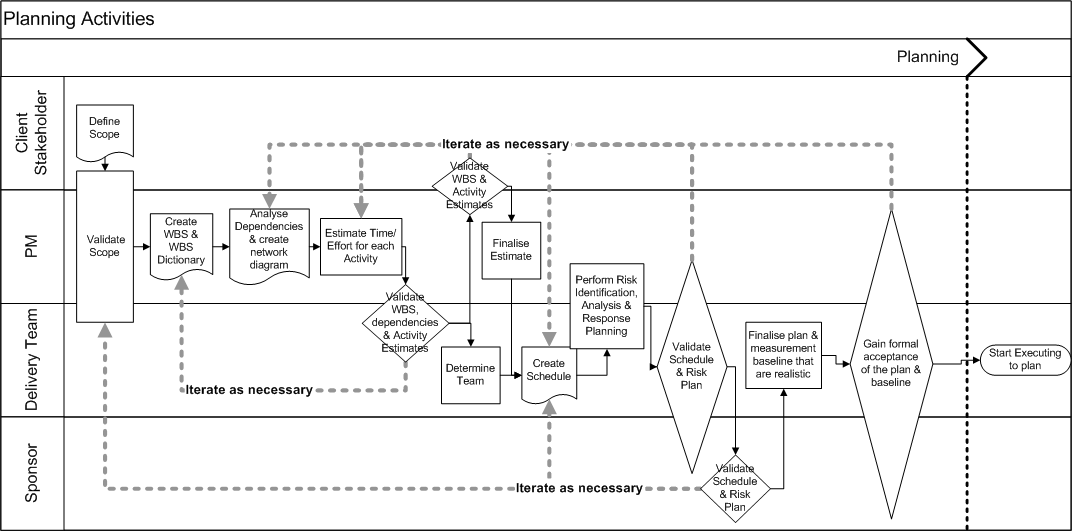
Goals
Students learn how to develop a project timeline and allocate project resources using either the traditional or agile methodology.
Students can determine feasibility of each, and explain which one they would choose for a particular project.
Traditional method
- Determine project phases (analysis, design, etc), tasks (brainstorm, concept, design, development) and outputs (wireframes, design mock-ups etc) that have to be done in each.
- Work with team members to estimate the amount of work each tasks will take. Note any assumptions or constraints. Assign resource to each task.
- Draw up a Gantt chart, a network diagram or timeline. You may use a project management tool to generate this.
- Identify internal and external dependencies, and any critical paths and near-critical paths.
- Identify key milestones, including required meetings: client reviews, client hand-offs
- Briefly describe how the timeline, and therefore the project would be affected if a client is late with one of their deliverables (e.g. providing copy)
Bonus points:
- Identify internal deliverables of tasks on the timeline
- Briefly describe what kind of projects is best suited to waterfall (and why), and when it is necessarily to adapt the simple waterfall model for a more iterative development.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project phases | All project phases and tasks are clearly defined and complete. | Project phases and tasks are mostly defined. | Some project phases are defined and some tasks are defined. | Some project phases are defined but project tasks missing. |
| Time estimation | All tasks have reasonable time estimations and all estimations are supported by project/scope assumptions. Reasoning and approach behind estimates are clearly and comprehensively documented. | All tasks have reasonable time estimations, some estimations supported by project/scope assumptions. Reasoning and approach behind estimates are clearly documented. | Tasks have questionable time estimations, some estimations supported by project/scope assumptions (which may also be incorrect or unreasonable). Reasoning and approach behind estimates are partially documented. | Tasks have unreasonable time estimations with no supporting project/scope assumptions. Reasoning and approach behind estimates are not well documented. |
| Resources | All tasks are assigned a resource. | Most tasks are assigned a resource. | Some tasks are assigned a resource. | Very few resources are assigned. |
| Timeline/roadmap | All tasks, deliverables, milestones, dependencies and time estimations are accounted for in the timeline. Critical paths are identified if applicable. Required internal meetings, client reviews and client-hand-off meetings are comprehensively noted. | All tasks, deliverables, milestones, dependencies and time estimations are accounted for in the timeline. Critical paths are identified if applicable. Some internal meetings, client reviews and client hand-off meetings are noted. | Most tasks, deliverables, milestones, dependencies and time estimations are accounted for in the timeline. Critical paths, internal meetings, client reviews and client hand-off meetings are not comprehensively noted. | Some tasks, deliverables, milestones, dependencies and time estimations are accounted for in the timeline. Critical paths, internal meetings, client reviews and client hand-off meetings are not comprehensively noted. |
| Timeline adjustment scenario | Description mentions correct shifts on the timeline that are required and impact on project delivery. Description also mentions communicating the impact to the team. | Description mentions correct shifts on the timeline that are required and impact on project delivery. | Description mentions shifts on the timeline that are partially correct and impact on project delivery. | Description mention shifts on the timeline that are partially correct. |
| Internal deliverables (bonus) | - | - | All internal deliverables of tasks are noted. | Some internal deliverables of tasks are noted. |
| Suitability (bonus) | - | - | Projects/workstreams most suited to the waterfall model are identified. Reasoning correct and complete. | Projects/workstreams most suited to waterfall model are identified. Reasoning missing, incomplete or incorrect. |
Notes on rubrics: The main form of assessment is not that there is necessarily a right/wrong answer, more that the student understands the decisions they have made. Real projects sometimes require creative solutions, it’s more important that the student grasps the consequences project decisions rather than follow a rote waterfall model.
Agile method
- From the RFP, write a set of main user stories. Document any justifications, assumptions or constraints.
- Work with team members to estimate story points and an initial velocity. Document any assumptions on estimations. Assign resource to each story. If you cannot assign a resource, explain why.
- Draw up a roadmap or end-to-end plan, showing what’s going to be on at which iteration. Identify how/when each iteration will be full initiated, planned, executed and closed. You may use a scrum/agile development management tool to generate this.
- Identify points where design & UX design would have to take place for relevant stories
- Identify key milestones/releases
- Briefly describe how you would adjust the stories in each iteration after you have established a steady velocity
Bonus points
- Identify internal deliverables based on user stories.
- Briefly describe what kind of projects is best suited to agile, and why.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User stories | User stories are complete. Priorities are adequately supported by justifications and assumptions. | User stories are reasonably complete. Priorities are partially supported by justifications and assumptions. | User stories are somewhat complete. Priorities are not adequately supported by justifications and assumptions. | User stories are incomplete. Assumptions and justifications are missing or inadequate. |
| Time estimation / velocity | All user stories have reasonable story points and are supported by comprehensive and clearly documented assumptions. Velocity is correctly calculated. | All user stories have reasonable story points and some estimations supported by clearly documented assumptions. Velocity is correct calculated. | User stories have questionable story points and some estimations supported by assumptions (which may also be incorrect or unreasonable). Velocity is included but may or may not be correct. | User stories have unreasonable time estimations with no supporting assumptions. Velocity is included but incorrect. |
| Resources | All user stories are assigned a resource. Or, if a few user stories are not assigned resources, justification is provided. | Most user stories are assigned a resource. If a few user stories are not assigned resources, justification is provided. | Some user stories are assigned a resource, and justification is provided. | Few user stories are assigned a resource, and inadequate or no justification is provided. |
| Roadmap | All user stories correctly set out in appropriate iterations. Key milestones are noted. Points where design efforts are required are noted. | All user stories correctly set out in appropriate iterations. Key milestones are noted. Points where design efforts are required are partially indicated. | Most user stories correctly set out in iterations. Key milestones and points where design efforts are required are not comprehensively noted. | Some user stories correctly set out in iterations. Key milestones and points where design efforts are required are not comprehensively noted. |
| Adjusting velocity | Description mentions how more or less stories are placed in particular iterations, and describes impact on key milestones. Description also mentions communicating the impact to the team. | Description mentions how more or less stories are placed in particular iterations, and describes impact on key milestones. | Description mentions how more or less stories are placed in particular iterations, and partially describes impact on key milestones. | Description mentions how more or less stories are placed in particular iterations. |
| Internal deliverables (bonus) | - | - | All internal deliverables of user stories are noted. | Some internal deliverables of user stories are noted. |
| Suitability (bonus) | - | - | Projects/workstreams most suited to agile development are identified. Reasoning correct and complete. | Projects/workstreams most suited to agile development are identified. Reasoning missing, incomplete or incorrect. |
Chinese Whispers/Telephone
Assignment: Chinese whispers/telephone
Section: Project Management
Phase: Initiation, Completion
Type: Group roleplay/activity
Overview
The chinese whispers/telephone game is a great method to illustrate how easily communication can breakdown and how costly the effects can be. The exercise will also cover as well as the importance of buy-in and documenting decisions and changes made during the course of the project. Through the exercise, students will be exposed to and practice principles of change management.
Goals
- Students understand the difference between authoritative information and rumour and how to distinguish between them.
- Students are reminded first-hand how communication can easily be misinterpreted through multiple parties.
- Students learn to anticipate and plan for change and build adaptive courses of action based on anticipated changes.
- Students practice listening and communication skills.
- Students learn through interaction and a fun activity.
- Students create connections with each other through activity and a common goal.
- Students begin to feel a sense of community with each other.
Readings
Useful quote: “If it’s not in writing, it’s a rumour; and we don’t work that way.”
Practice
1. Standard. Instructor gives first student three critical things to remember about the project. Student passes it on.
2. Enhanced. Instructor gives first student three critical things to remember about the project. Student passes it on. Instructor adds an additional 2 somewhere down the line (analogous to client wanting to add to project requirements or addition from major stakeholders). Students have to remember the original 3, plus the additional new two.
3. Advanced. Instructor gives first student three critical things to remember about the project. student passes it on. Instructor changes 1-2 of original 3 and also adds an additional 2 somewhere down the line (analogous to client wanting to add to project requirements or addition from major stakeholders). Students have to remember and accurately relay all information.
4. Last person has to report their message. However, in addition, all participants must discuss the last message and determine where the change happens. Once the original message is figured out, then the request needs to be either agreed upon, or negotiated and then documented.
5. Group discussion Students share their experience in the game and also from professional experience. Students troubleshoot the process of the game see how they can improve it. Instructor makes parallels to actual PM situations.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise participation | Actively engages in exercise with interest and attention. | Engages in exercise with moderate interest and attention. | Engages in exercise with low interest and attention. | Engages in exercise with little or no interest and attention. Distant and removed from activity. |
| Discussion participation | Listens well to other group members. Provides useful ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Not afraid to challenge an idea constructively. | Listens moderately well to other group members. Provides some ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Challenges ideas constructively, though moderately so. | Listens moderately well to other group members. Provides only a few ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Little challenge of ideas constructively or otherwise. | Does not listen to other group members. Provides neither ideas nor feedback during participating in the group discussion. Aggressively and negatively challenges ideas. |
| Fairness in participation | Does not dominate discussion while being an active participant. Shows guidance and leadership qualities. | Does not dominate discussion while being a moderately active participant. Displays moderate leadership qualities. | Does not dominate discussion, but only participates minimally. | Is overbearing or domineering to discussion or does not participate in discussion. |
| Respect to others | Respects others’ need to express their opinions. | Displays moderate respects of others’ need to express their opinions. | Displays low respects of others’ need to express their opinions. May exhibit some rudeness towards group members. | Disrespectful of others’ need to express their opinions and is rude to group members |
Project Kickoff
Assignment: Project Kickoff
Section: Client Management
Phase: Kickoff
Type: project support documentation (to facilitate the progress of the project or manage deliverables)
Overview
You are given a preliminary overview of the project, and have to plan for the project kickoff meeting. Write up the meeting agenda with what you are going to cover, and what questions you need to ask the client to be clear about how the project should progress and what will make the project a success for the both parties.
Goals
- Develop/promote sense of team cooperation
- Evaluate team members’ strengths and weaknesses
- Demonstrate ability to help client clarify priorities
Readings
- Scrappy Project Management, ch.2, 10
- Web Project Management, ch.8
- Making Things Happen, ch.3, 10
Practice
- Present project brief, project timeline and scope, and acceptance criteria. Present project roles and high level risks/assumptions.
- Demonstrate ability to run an efficient meeting: identify meeting goals, critical message, troubleshoot and garner action steps.
- Produce professional materials and accurate meeting minutes.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meeting agenda | Meeting objectives are clearly defined, items of discussion are listed and written in an actionable manner. | Meeting objectives are reasonably clearly stated, items of discussion are listed. | Meeting objectives are vague, items of discussion are incomplete and somewhat actionable. | Meeting objectives not specific enough, items of discussion are not actionable. |
| Presentation of project overview/summary | Presentation is clear and to the point, clearly describing the project foundations and objectives. The project overview is clearly communicated, including the initial desires of the client and goals of the implementing company. | Presentation is reasonably clear and to the point, describing the project foundations and objectives. The project overview is communicated, including the initial desires of the client and goals of the implementing company. | Presentation is average, not very comprehensive or clear, describing the project foundations and objectives. The project overview is mostly communicated, including the initial desires of the client and goals of the implementing company. | Presentation is long-winded, covers only some of the project foundations and objectives but is incomplete. The project plan is communicated, but initial desires of the client and goals of the implementing company are not made clear. |
| Presentation of project scope | Presentation is clear and to the point, fully describing what is encompassed in the project. The project scope is clearly communicated, including the multiple components of the project. | Presentation is reasonably clear and to the point, mostly describing what is encompassed in the project. The project scope is communicated, including the multiple components of the project. | Presentation is average, not very comprehensive or clear, describing what is encompassed in the project. The project scope is mostly communicated, including the multiple components of the project. | Presentation is long-winded, and covers only some of what is encompassed in the project but is incomplete. The project scope is only partially communicated, and the multiple components of the project are unclear. |
| Presentation of project timeline | Presentation is clear and to the point, clearly describing the project schedule. The project timeline is clearly communicated, including the major milestones, presentations, meetings, and handoffs. | Presentation is reasonably clear and to the point, describing the project schedule. The project timeline is communicated, including the major milestones, presentations, meetings, and handoffs. | Presentation is average, not very comprehensive or clear, describing the project schedule. The project timeline is mostly communicated, including milestones, presentations, meetings, and handoffs. | Presentation is long-winded, covers only some of the project schedule but is incomplete. The project timeline is communicated, but only partially, while milestones, presentations, meetings, and handoffs are not made clear. |
| Presentation of project roles | Presentation is clear and to the point, with clear communication of the project roles of the key players. | Presentation is reasonably clear and to the point, with communication of the project roles of the key players. | Presentation is average, not very comprehensive or clear; project roles are mostly communicated. | Presentation is long-winded, covers only some of the project roles but is incomplete. The project roles are only partially communicated and are not entirely clear. |
| High level risks/assumptions | Presentation is clear and to the point, with clear communication of the high level risks/assumptions of the project. | Presentation is reasonably clear and to the point, with communication of the high level risks/assumptions of the project. | Presentation is average, not very comprehensive or clear; the high level risks/assumptions of the project are mostly communicated. | Presentation is long-winded, covers only some of the project roles but is incomplete. The the high level risks/assumptions of the project are only partially communicated and are not entirely clear. |
| Discussion of project acceptance criteria | Discussion of acceptance criteria is efficient and criteria is determined. Student effectively listens to, processes, and responds to relevant information. Tries to keep people working well together. | Discussion of acceptance criteria is mostly efficient and criteria is eventually determined. Student listens to, processes, and responds to relevant information. Does not cause “waves” in the group. | Discussion of acceptance criteria is somewhat efficient and criteria is eventually determined but it takes a while. Student mostly listens to, processes, and responds to relevant information, but sometimes is not a good team member. | Discussion of acceptance criteria is inefficient and disorganized and criteria is not determined. Rarely listens to, processes, and responds to relevant information, but is not a good team player. |
| Ability to run meeting efficiently | Meeting is kept on track and on time, all points are covered, and all action points are assigned. | Meeting runs over time, all points are covered and all action points are assigned. | Meeting runs over time, most points are covered, some action items established. | Meeting runs over time, not all points are covered and action points are not explicitly developed or assigned. |
| Clarity of communication (verbal) | The verbal explanations of the project process is clear, easy to understand, and follows a natural progression. | The verbal explanations of the project process is fairly clear, moderately understandable, and mostly follows a natural progression. | The verbal explanations of the project process is only partially clear and understandable, and only slightly follows a natural progression. | The verbal explanations of the project process is unclear, is not understandable, and does not follow a natural progression. |
| Clarity of communication (materials) | The presentation documents are well-organized, consistently formatted, and has a very professional presentation/look and feel. | The presentation documents are mostly organized and consistently formatted, and has a moderately professional presentation/look and feel. | The presentation documents are only somewhat organized and consistently formatted, and has a slight professional presentation/look and feel. | The presentation documents are poorly organized and inconsistently formatted, and completely lacks a professional presentation/look and feel. |
| Meeting minutes | Minutes are readable, comprehensive, mentioning attendees, problems raised, solutions decided upon and clear action points assigned to team members. | Minutes are readable and fairly comprehensive, mentioning some problems raised, solutions decided upon, and clear action points. | Minutes are fairly readable but not comprehensive, mentions some problem raised, some solutions decided upon and lacking clear action points. | Minutes are unclear, and not comprehensive, missing problems raised, solutions decided upon and lacking action points. |
Communication Quadrant
Assignment: Communication Quadrant
Section: Client Management
Phase: Kickoff
Type: Role Play/Group Activity
Overview
As a project manager, you will have to deal with various different personality types and have to communicate information to a lot of different people. Understanding a person’s communication style will help you tailor the message in a way that your audience will best receive it and take the desired actions.
Students will self-identify which area of the quadrant they are in, and then practice communicating same message about the status of the project (set-back, change, or difficult issue) to members of each quadrant in a manner appropriate to that group.
Reading
Leadership Styles: A Behavioral Matrix by Susan Sayers
Goals
- Students identify their own communication style
- Students identify the communication style of their team members
- Students learn to adapt their message to their audience
- Students create and build connections with each other as a group/team
Practice
- Instructor explains and illustrates the different communication quadrants. The room is divided into four areas representing each quadrant.
- Students arrange themselves into the quadrants that they feel best reflect their own behaviors.
- Instructor gives more information on each quadrant type, and also checks with the members of the quadrant to see that the description is accurate.
- Instructor describes different ways of communicating the same message to each of the different quadrants.
- Instructor gives the students 3 scenarios:
- the project launch date has be pushed back due to development problems
- the client’s desired change will cause an increase in the project cost and will result in a change order
- the client’s consultant project manager is a communication bottleneck and is adversely affecting the project
- Students brainstorm within their groups and determine 4 different ways to communicate the messages.
- Members of the different quadrants give feedback on the effectiveness of the communication, and give suggestions on improvement
- Whole class discusses what felt most comfortable, what felt most uncomfortable, and how they will use this information in the future.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise participation | Actively engages in exercise with interest and attention. | Engages in exercise with moderate interest and attention. | Engages in exercise with low interest and attention. | Engages in exercise with little or no interest and attention. Distant and removed from activity. |
| Discussion participation | Listens well to other group members. Provides useful ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Not afraid to challenge an idea constructively. | Listens moderately well to other group members. Provides some ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Challenges ideas constructively, though moderately so. | Listens moderately well to other group members. Provides only a few ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Little challenge of ideas constructively or otherwise. | Does not listen to other group members. Provides neither ideas nor feedback during participating in the group discussion. Aggressively and negatively challenges ideas. |
| Fairness in participation | Does not dominate discussion while being an active participant. Shows guidance and leadership qualities. | Does not dominate discussion while being a moderately active participant. Displays moderate leadership qualities. | Does not dominate discussion, but only participates minimally. | Is overbearing or domineering to discussion or does not participate in discussion. |
| Respect to others | Respects others’ need to express their opinions. | Displays moderate respects of others’ need to express their opinions. | Displays low respects of others’ need to express their opinions. May exhibit some rudeness towards group members. | Disrespectful of others’ need to express their opinions and is rude to group members. |
Internal Project Kickoff Meeting
Assignment: Internal project kickoff meeting
Section: Team management
Phase: Kickoff
Type: Role-play
Class organisation
The teacher assigns rotating roles of class members to create teams that include at least:
- one project manager
- one graphics designer
- one user experience designer
- one front-end engineer
- one back-end developer
Goals
Students practice how to communicate a project’s goals to a team, get feedback on the schedule and establish accountability for deliverables.
Readings
- Meeting: Responding to RFP (Sample meeting agenda)
- Web Project Management, Chapter 8
- Making Things Happen, Chapter 10
Assignment
Prior to the meeting, the project manager sends out a meeting agenda.
The project manager presents the project description and project plan, including accountabilities, and assigns someone to take meeting minutes.
Working with the team, establish how realistic the project plan is for each deliverable.
Assignment outcome
Meeting minutes of which changes have been made to the original project plan as well as additional questions and assumptions that arise to feed back to the client.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presentation | Presentation is clear and to the point, clearly describing the project problem and proposed solution. The project plan is clearly communicated, including who is accountable for which tasks, when tasks need to be done by, how we know they are completed satisfactorily. | Presentation is reasonably clear and to the point, describing the project problem and proposed solution. The project plan is communicated, including who is accountable for which task, when tasks need to be done by, how we know they are completed satisfactorily. | Presentation is average, not very comprehensive or clear, describing the project problem and proposed solution. The project plan is communicated, including who is accountable for which tasks, when tasks need to be done by, how we know they are completed satisfactorily. | Presentation is long-winded, covers some description of the project problem and proposed solution but is somewhat incomplete. The project plan is communicated, but assignments, tasks timelines and quality criteria are not made clear and explicit. |
| Meeting agenda | Meeting objectives are clearly defined, items of discussion are listed and written in an actionable manner. | Meeting objectives are reasonably clearly stated, items of discussion are listed. | Meeting objectives are vague, items of discussion are incomplete and somewhat actionable. | Meeting objectives not specific enough, items of discussion are not actionable. |
| Meeting management | Meeting is kept on track and on time, all points are covered, and all action points are assigned. | Meeting runs over time, all points are covered and all action points are assigned. | Meeting runs over time, most points are covered, action items established. | Meeting runs over time, not all points are covered and action points are not explicitly stated. |
| Meeting minutes | Minutes are readable, comprehensive, mentioning attendees, problems raised, solutions decided upon and clear action points assigned to team members. | Minutes are readable and fairly comprehensive, mentioning some problems raised, solutions decided upon, and clear action points. | Minutes are fairly readable but not comprehensive, mentions some problem raised, some solutions decided upon and lacking clear action points. | Minutes are unclear, and not comprehensive, missing problems raised, solutions decided upon and lacking action points. |
| Contribution | Routinely provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Not afraid to challenge an idea constructively. A definite leader who contributes a lot of effort. | Usually provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Hesitant to challenge ideas. A strong group member who tries hard. | Sometimes provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Does not challenge existing ideas. A satisfactory group member who does what is required. | Rarely provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. May refuse to participate. |
| Working with others | Almost always listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others. Tries to keep people working well together. | Usually listens to, shares, with, and supports the efforts of others. Does not cause “waves” in the group. | Often listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others, but sometimes is not a good team member. | Rarely listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others. Often is not a good team player. |
Continual Project Assessment
Assignment: Continual project assessment
Section: Project management
Phase: Implementation
Type: Group/role-play / project support documentation
Goals
Students learn to communicate project progress with internal team members and preparing communications for external clients.
Readings
- Meeting: Responding to RFP (Sample meeting agenda)
- Web Project Management, Ch 8 (meetings) & 12 (case study).
- Making Things Happen, p205. (Example of good email)
- Making Things Happen, Chapter 10
Optional resource: Project report template
Part 1
The design for a key feature (choose one) has taken two days longer than first estimated.
- Update your project plan to reflect the project status.
- Set up an agenda for the team meeting.
- With a team, communicate and discuss what needs to be done for the week.
- Reiterate major deliverable dates
- Identify risks (e.g. this delay impacts development time), and how your team can work to get around this problem.
Write a summary message of this meeting to your team.
Part 2
A client has indicated new features need to be included, but the timeline cannot change. Identify risks with your team, and discuss what you will do to address this issue.
Write a summary message to the client.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contributions | Routinely provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Not afraid to challenge an idea constructively. A definite leader who contributes a lot of effort. | Usually provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Hesitant to challenge ideas. A strong group member who tries hard. | Sometimes provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Does not challenge existing ideas. A satisfactory group member who does what is required. | Rarely provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. May refuse to participate. |
| Working with others | Almost always listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others. Tries to keep people working well together. | Usually listens to, shares, with, and supports the efforts of others. Does not cause “waves” in the group. | Often listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others, but sometimes is not a good team member. | Rarely listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others. Often is not a good team player. |
| Meeting agenda | Meeting objectives are clearly defined, items of discussion are listed and written in an actionable manner. | Meeting objectives are reasonably clearly stated, items of discussion are listed. | Meeting objectives are vague, items of discussion are incomplete and somewhat actionable. | Meeting objectives not specific enough, items of discussion are not actionable. |
| Meeting management | Meeting is kept on track and on time, all points are covered, and all action points are assigned. | Meeting runs over time, all points are covered and all action points are assigned. | Meeting runs over time, most points are covered, action items established. | Meeting runs over time, not all points are covered and action points are not explicitly stated. |
| Summary message to team | Summary is readable, comprehensive, mentioning attendees, problems raised, solutions decided upon and clear action points assigned to team members. | Summary is readable and fairly comprehensive, mentioning some problems raised, solutions decided upon, and clear action points. | Summary is fairly readable but not comprehensive, mentions some problem raised, some solutions decided upon and lacking clear action points. | Summary is unclear, and not comprehensive, missing problems raised, solutions decided upon and lacking action points. |
| Summary message to client | Summary is readable and concise, clearly reiterating the issue, and the team’s proposed solution. Summary indicates clearly what the next steps will be. | Summary is readable and concise, clearly reiterating the issue, and the team’s proposed solution. | Summary is fairly readable (too long or too short), does not reiterate the issue, but states the team’s proposed solution. | Summary is unclear (too long or too short), does not reiterate the issue nor clearly states the team’s proposed solution. |
Conflict Resolution
Assignment: Conflict Resolution
Section: Client Management
Phase: Implementation
Type: Group roleplay/activity
Overview
There are members involved with the project who obscure, confuse, and inappropriately aggrandize information which is adversely affecting the flow of the project and effective interaction. The PM needs to devise methods to diffuse tension and resolve conflict to get the project to more easily see completion.
Goals
- Demonstrate ability to work in groups/teams for a common goal
- Communicate clearly and effectively verbally
- Develop interpersonal skills to help teams work together better
- Understand and actively choose an appropriate response style
- Students practice listening and communication skills
Readings
- Scrappy Project Management, ch.3
- Making Things Happen, ch.9, 11, 16
- Article:Project Management - Tips for Conflict Resolution -Martin Burns
Practice
Generate and discuss different options for ways to deal resolving conflict due to either outside vendors/consultants, difficult clients, or recalcitrant team members. Focus on win-win solutions and shifting the communication dynamic to the positive.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discussion participation & idea generation | Listens well to other group members. Provides useful ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Not afraid to challenge an idea constructively. | Listens moderately well to other group members. Provides some ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Challenges ideas constructively, though moderately so. | Listens moderately well to other group members. Provides only a few ideas and feedback during participating in the group discussion. Little challenge of ideas constructively or otherwise. | Does not listen to other group members. Provides neither ideas nor feedback during participating in the group discussion. Aggressively and negatively challenges ideas. |
| Fairness in participation | Does not dominate discussion while being an active participant. Shows guidance and leadership qualitites. | Does not dominate discussion while being a moderately active participant. Displays moderate leadership qualities. | Does not dominate discussion, but only participates minimally. | Is overbearing or domineering to discussion or does not participate in discussion. |
| Respect to others | Respects others’ need to express their opinions. | Displays moderate respects of others’ need to express their opinions. | Displays low respects of others’ need to express their opinions. May exhibit some rudeness towards group members. | Disrespectful of others’ need to express their opinions and is rude to group members. |
Skills Evaluation
Assignment: Skills evaluation
Section: Team management
Phase: Implementation
Type: Group/role-play
Goals
Students self-evaluate and investigate what they consider their skills, strengths and weaknesses.
Assignment
In groups of 4 or 5, write down a list of your skills, strengths and weakness.
Discuss with each other:
- past experiences that leads you to believe why you are good or bad at something
- what you would like to get better at
- what steps you can take to get better at certain skills
Rubrics
Grade on attendance and participation.
Notes
This assignment can be done twice: beginning of the term/semester and at the end of the term/semester.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contribution | Routinely provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Not afraid to challenge an idea constructively. A definite leader who contributes a lot of effort. | Usually provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Hesitant to challenge ideas. A strong group member who tries hard. | Sometimes provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. Does not challenge existing ideas. A satisfactory group member who does what is required. | Rarely provides useful ideas when participating in the group and in classroom discussion. May refuse to participate. |
| Working with others | Almost always listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others. Tries to keep people working well together. | Usually listens to, shares, with, and supports the efforts of others. Does not cause “waves” in the group. | Often listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others, but sometimes is not a good team member. | Rarely listens to, shares with, and supports the efforts of others. Often is not a good team player. |
Handoff, Review & Acceptance
Assignment: Handoff, Review & Acceptance
Section: Client Management
Phase: Implementation
Type: Created document (to be seen by “client”)
Overview
Your team has completed a major milestone and there is a deliverable to the client. However, timely feedback on this deliverable is critical for the continuation of the project and the subsequent deliverables are dependent upon it. You need to communicate all of this information to the client in order to get them to act within the desired timeframe.
Goals
- Clearly communicate the necessity of deliverable and its importance in the grand scheme of the project, particularly where it’s a dependency of other tasks or project payment.
- Differentiate between “handoff for review” and “handoff for Acceptance”.
- Establish clear objectives for the client.
- Establish clear time constraints for the client and what happens if they’re not met.
Practice
- Write up a handoff memo to give a client an important deliverable that they need to review and give feedback on in a limited period of time. Make the time constraints and the consequences of deviating from them explicit.
- Clearly explain deliverable, its content, relevance to the project, and location/how to access it
- Clearly communicate the action items with the deliverable, as well as their need and their dependencies on upcoming tasks. Make repercussions for not achieving the action items very clear. For example, one approach is that if comments not returned by agreed date, deliverable is deemed Accepted.
- Present/reiterate acceptance criteria (determined during the project kickoff)
- Define the feedback mechanism (e.g. document template, review site, commenting in document, etc.) and how any comments are adopted into rework
- Reiterate project timeline
- Outline the next steps for the project, as well as responsibilities for upcoming tasks.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deliverable explanation | The deliverable, its content, relevance to the project, dependencies, and location/how to access are clearly communicated. | The deliverable, its content, relevance to the project, dependencies, and location/how to access are moderately communicated. | The deliverable, its content, relevance to the project, dependencies, and location/how to access are somewhat communicated. | The deliverable, its content, relevance to the project, dependencies, and location/how to access are unclear. |
| Action items | All relevant action points are communicated, as well as their need and their dependencies on upcoming tasks. Repercussions for not achieving them is made very clear. | All relevant action points are moderately communicated as well as their need and their dependencies on upcoming tasks. Repercussions for not achieving them are made moderately clear. | All relevant action points are mostly communicated as well as their need and their dependencies on upcoming tasks. Repercussions for not achieving them are made somewhat clear. | Action points are not communicated nor is their need and their dependencies on upcoming tasks. Repercussions for not achieving them are unclear. |
| Timeframe | The project timeline is clearly communicated. | The project timeline is moderately communicated. | The project timeline is mostly communicated. | The project timeline is only partially communicated if at all. |
| Next steps for project | The next steps for the project are clearly communicated, as well as responsibilities for upcoming tasks. | The next steps for the project are moderately communicated, as well as responsibilities for upcoming tasks. | The next steps for the project are somewhat communicated, as well as responsibilities for upcoming tasks. | The next steps for the project are not communicated, nor as responsibilities for upcoming tasks. |
Weekly Status Reports
Assignment: Weekly Status Reports
Section: Client Management
Phase: All
Type: Created document (to be seen by “client”, and manager)
Overview
Project managers need to provide weekly progress reports to clients/managers (the instructor) to summarize the work of the group for the week.
Goals
- Communicate effectively and consistently with all project members, both internal and external
- Demonstrate continual project assessment
- Demonstrate continual personal and team assessment
Readings
Web Project Management, ch.8
Optional Resource
Practice
In the form of a blog post write up a brief account of the project. This should include:
- tasks for the current week and what was accomplished
- tasks and goals for the upcoming week with baseline & forecast dates
Your assessment should include:
- Summary Status: 1-2 brief paragraphs.This is your elevator pitch of the week and may be the message that gets more widely communicated.
- Milestones hit/log of milestones, with baseline date, plus actual or forecast date as appropriate.
- Current Risk Log, with weighting
- Current Action Log - this is where you ask for help from your stakeholders & hold them to account to deliver. Be sure to indicate due date & who is accountable for each action
- Any changes in the project scope and/or schedule and/or Quality and/or cost, and notation of any formal change requests & their status
- Any client requests, meetings and decisions made.
A further self-assessment needs to be done with regard to the assignments, especially the interactive ones, and what each student feels they learned from the assignment and how the assignment could have been more valuable for them.
| Category | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This week | Tasks for the current week and what was accomplished is clearly communicated and outlined, including milestones hit, any changes in the project scope and/or schedule, any client requests, meetings and decisions made; an overview of each team member’s contributions and responsibilities. | Tasks for the current week and what was accomplished is moderately communicated and outlined, including milestones hit, any changes in the project scope and/or schedule, any client requests, meetings and decisions made; an overview of each team member’s contributions and responsibilities. | Tasks for the current week and what was accomplished is somewhat communicated and outlined, including milestones hit, any changes in the project scope and/or schedule, any client requests, meetings and decisions made; an overview of each team member’s contributions and responsibilities. | Tasks for the current week and what was accomplished is unclear and poorly outlined, including milestones hit, any changes in the project scope and/or schedule, any client requests, meetings and decisions made; an overview of each team member’s contributions and responsibilities. |
| Next week | Tasks for the upcoming week and what is to be accomplished is clearly communicated and outlined, including u
Examination QuestionsThere are no examination questions for this course. ResourcesThere are no additional resources for this course. Please see the Assignments for the corresponding recommended readings. Learning ModulesHelp us develop our living curriculum. Contribute a learning module.ContributorsPrimary Course Developers: Denise Jacobs and Stephanie Troeth. Course Reviewer: Martin Burns. |